Right Bundle Branch Block
Criteria
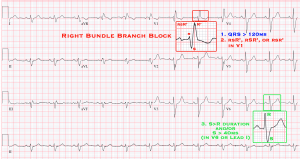
- QRS > 120 ms in adults (>100 ms in children 4-16yo, and > 90 ms <4yo
- Leads V1 or V2:
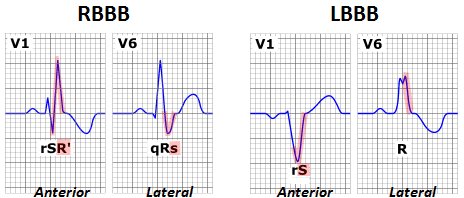
- rsr’ , rsR’ , or rSR’ pattern
- The R or r deflection is usually wider than the initial R wave.
- A wide and notched R wave pattern may be seen in lead V1 and/or V2.
- Leads 1 and V6: S > R in duration OR >40 ms in leads I and V6 in adults.
- R-wave Peak Time (When a pure dominant R wave with or without a notch is present in V1)
- Normal in V5/6, but >50 ms in V1
Examples
Left Bundle Branch Block
Criteria
- QRS ≥ 120ms in adults (>100ms children 4-16, >90ms children <4yo)
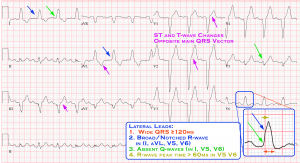
- Lateral Leads (I, aVL, V5, V6)
- Broad notched/slurred R-wave in LATERAL leads (I, aVL, V5, V6) (Sometimes V5-6 can have RS pattern, due to displaced transition of QRS)
- Absent q-waves in LATERAL LEADS (I, V5, V6) (aVL may have q)
- R-wave peak-time WIDE in LATERAL > 60ms in V5-6 (Normal in V1-3)
- ST and T-waves usually opposite direction of QRS
- Positive concordance can be normal (Positive T-wave in leads with upright QRS)
- NOTE: Negative concordance is abnormal. (Depressed ST or T-waves in leads with negative QRS)
- Axis Deviation can be RIGHT, LEFT, or SUPERIOR
Examples
Left Anterior Fascicular Block
Criteria
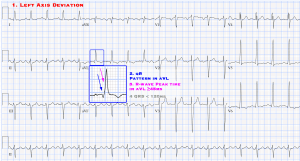
- Left Axis Deviation (-45° and -90°)
- qR pattern in lead aVL.
- R-peak time in lead aVL ≥45 ms.
- QRS < 120 ms.
Examples
Left Posterior Fascicular Block
Criteria
- Axis 90° to 180°
- rS pattern in leads I and aVL.
- qR pattern in leads III and aVF.
- QRS duration < 120 ms
Examples
Incomplete Left Bundle Branch Block
Criteria
- Same criteria as RBBB except: QRS 110-120ms (adultsL
Nonspecific Intraventricular Conduction Delay
Criteria
- QRS > 110ms
- Does not meet criteria for LBBB or RBBB OR Limb leads have LBBB pattern and precordial limbs have RBBB pattern (or vice versa
Further Reading
- Surawicz B, Childers R, Deal BJ, et al. AHA/ACCF/HRS recommendations for the standardization and interpretation of the electrocardiogram: part III: intraventricular conduction disturbances. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2009; 53(11):976-81.